Local Area Networks (LANs)
Martin McBride, 2017-10-06
Tags lan wan
Categories networks local area networks
A local area network, or LAN, is a network that connects a group of computers in a relatively small area, for example a single building or group of buildings. A school or office (or a home with several computers) would use a LAN to connect their computers.
A LAN will often connect to other devices, such shared printers, or a modem to access the Internet.
A LAN is usually owned and controlled by a single organisation. So, for example, if two different companies had an office in the same building, they would each have their own separate LAN.
A LAN doesn't have to be small - an office might contain hundreds of computers but would still be classed as a LAN if all the computers are on the same local network.
A typical LAN
A typical small LAN, such as a home network, might consist of a few connected devices. This might include:
- A few computers - desktops, laptops and tablet devices.
- Printers, scanners and other shared devices.
- A modem so that the computers can access the Internet.
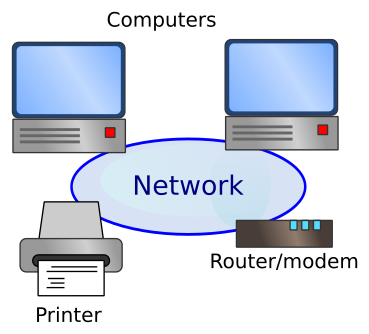
The devices might be connected by network cables, or in many cases might use wireless connections.
A school or office would be larger and might use different types of computers:
- ''workstations'' - ordinary desktop computers that people sit at to do their work.
- ''servers'' - more powerful computers dedicated to particular purposes, such as storing shared files or emails. These computers are usually accessed over the network, and might not even have a monitor and keyboard.
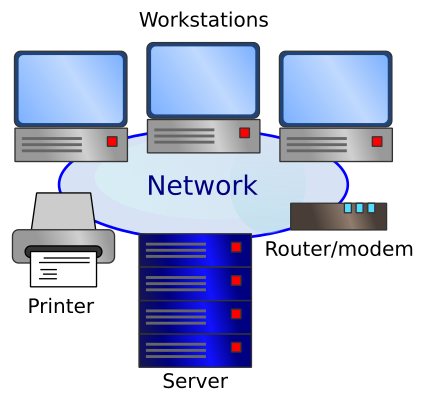
An larger office network will usually use wired connections, perhaps with a wireless access point for portable devices.
The benefits of a network
There are many benefits to networking. The main benefit is that it allows resources to be shared by different users, including:
- Files and folders can be shared between users more easily, rather than transferring files using memory sticks.
- Printers and other devices (such as scanners and 3D printers) can be used form any computer.
- The Internet connection, so all users can access email, the web, and other services.
There are other benefits:
- Software upgrades can be installed automatically across all the computers on the network.
- Anti-malware software can be kept up to date.
- Files stored on the file server can be backed up and archived centrally.
Disadvantages of a network
There are a few downsides to running a network:
- Viruses and other malware can spread quickly across the network.
- If the network has an Internet connection, hackers may be able to steal or destroy files.
- If the network fails, users might be unable to access their files on the server.
- Managing a network can be difficult and time consuming.
Wide area networks
By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) is used to link compute that are much further apart. For example, if a company had offices in different cities (or even different countries), they would need a WAN to allow all their computers to talk to each other.
On a LAN, the computers and devices are usually connected by Ethernet cables, or Wifi, which have quite a short range (typically less than 100m). A WAN uses other technologies to communicate over much greater distances.
Copyright (c) Axlesoft Ltd 2021